题目传送门:【CF888G】 Xor-MST
题目大意
$\ \ \ \ \ \ \,$给你一个 $n$ 个节点的完全图,第 $i$ 个点的权值为 $a_i$ ,两点的之间边权为这两个点权值的异或值,求最小生成树的权值。
想法
$\ \ \ \ \ \ \,$其实这道题没有那么复杂,还是好想的。
$\ \ \ \ \ \ \,$最小生成树的话,我们显然有一个基于贪心的$Kruskal$ 算法,复杂度 $O(n^2\log n)$,想想还是算了吧。
$\ \ \ \ \ \ \,$而遇到关于异或的题呢,我们一般会有两种想法:整形异或线性基,$Trie$ 树。
$\ \ \ \ \ \ \,$容易想到的,这道题当然和线性基没有关系了,我们思考一下 $Trie$ 树,首先,我们先把第一个样例从高位到低位插入线性基看看:
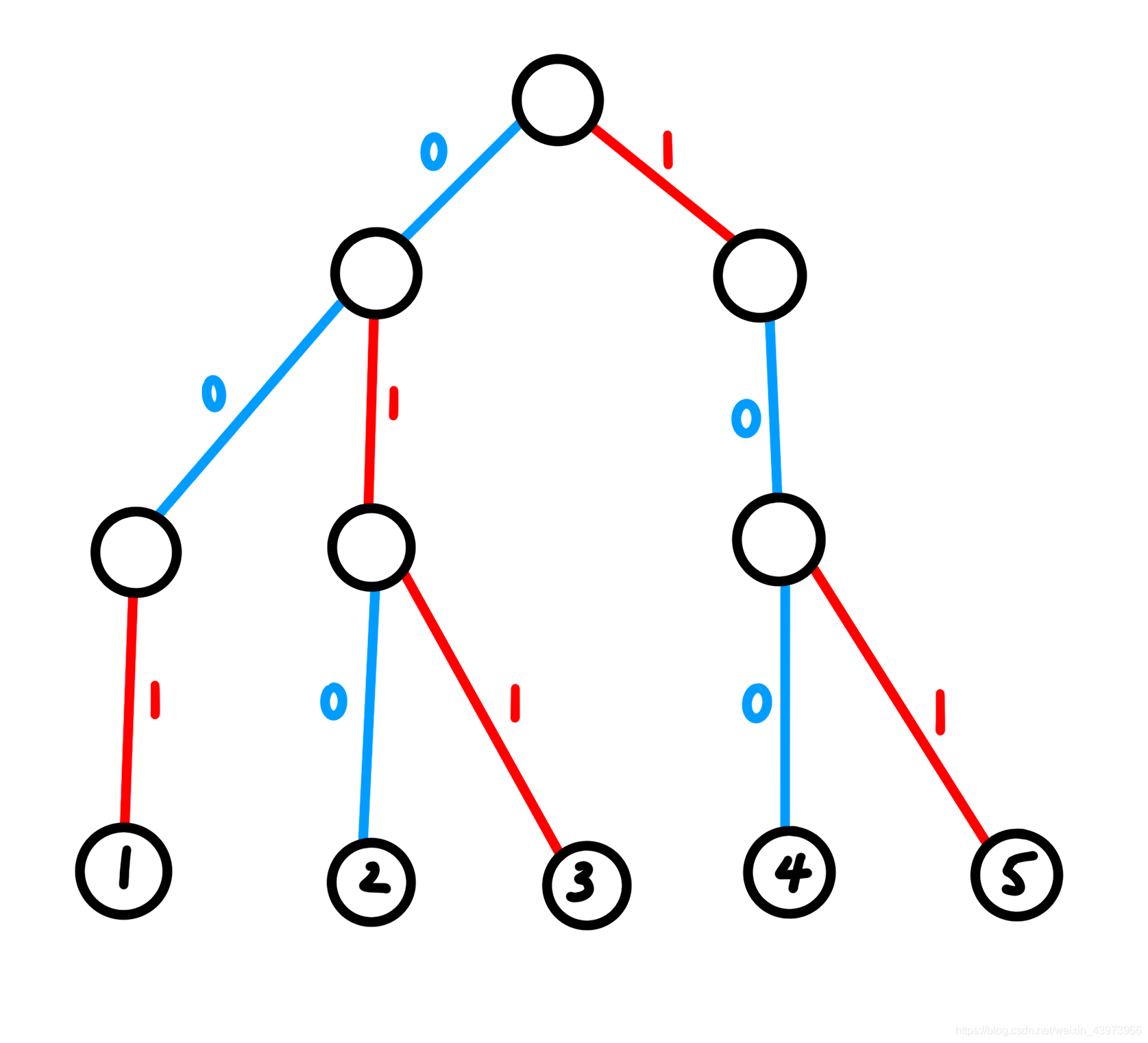
$\ \ \ \ \ \ \,$容易发现,对于每个叶子节点,既每个点值之间,要是需要互相连边,那么求 他们 $Lca$ 以后的边的亦或值 即可。
$\ \ \ \ \ \ \,$由此可得,若是 $Lca$ 的深度越深,便约优。因为我们是从高位到低位插入的,所以浅的点权值较大,要尽量避免选择浅的点。
$\ \ \ \ \ \ \,$我们不妨把可能是 $Lca$ 的点拉出来瞅瞅:
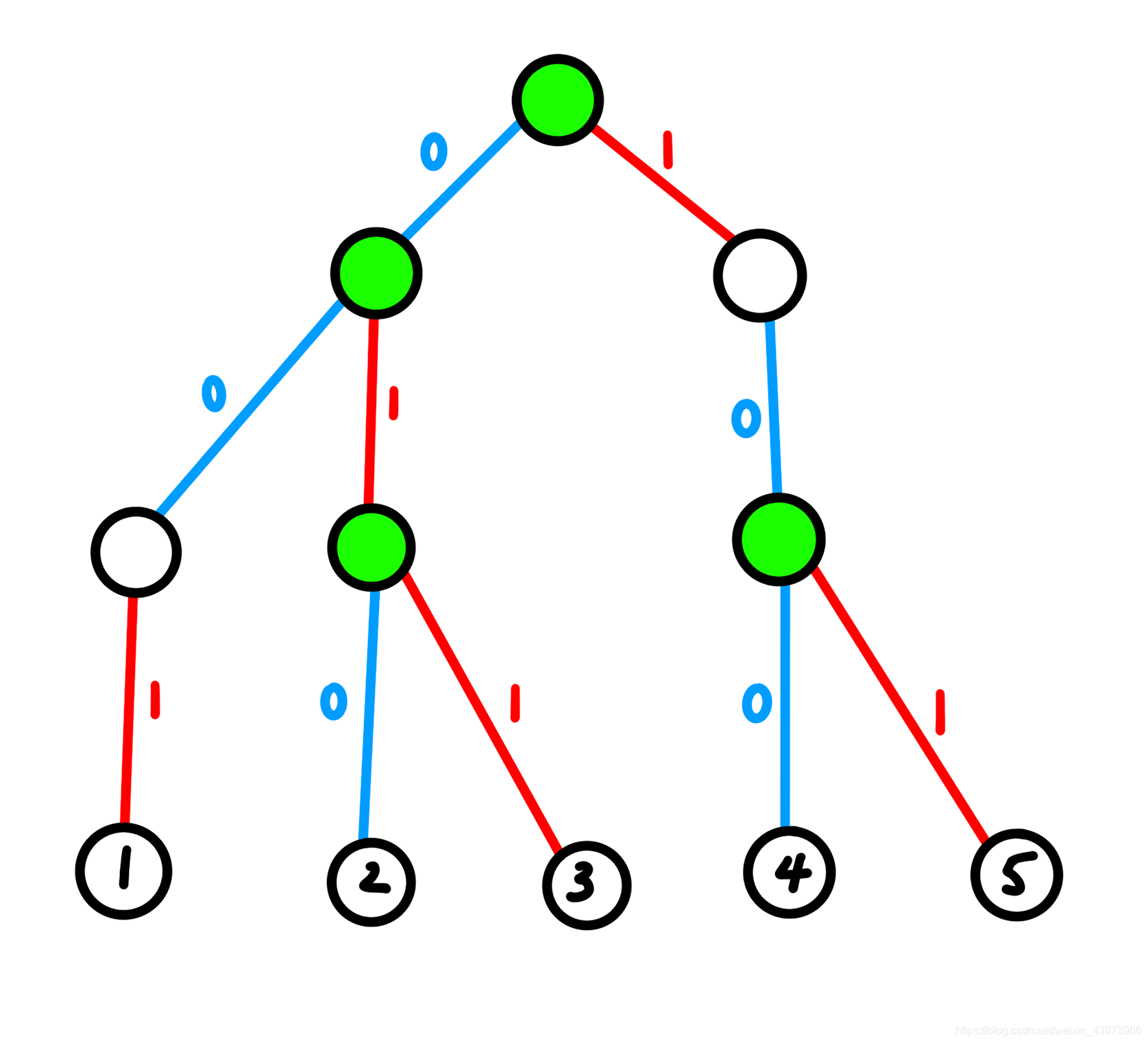
$\ \ \ \ \ \ \,$惊喜地发现,刚好有 $4$ 个点,也就是所有拥有两个儿子的点一共有 $4$ 个,可以证明,如果 $a_i$ 两两不等的话,那么这种点一共有 $n-1$ 个,那么答案就呼之欲出了:
$\ \ \ \ \ \ \,$我们每找到这样的点,就暴力贪心 $DFS$ 下去:
- 每次尽量同时走左儿子或右儿子;
- 如果两个都有,就两个都走,然后返回值取 $min$ 。
- 如果两个只有不一样的儿子,就在返回值加上这一深度$bit$的值,然后继续走
$\ \ \ \ \ \ \,$最终答案就是他们的 $DFS$ 值的和。
$\ \ \ \ \ \ \,$那如果 $a_i$ 不是两两不等的话怎么办呢,如果 $a_u=a_v$ 的话,我们当然首先建一条边连接 $u$,$v$,权值为 $0$,对答案完全没有影响,所以我们正常建,正常搜,是不会有问题的。
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| #include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
const int inf=0x7fffffff;
const double eps=1e-10;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;char ch;ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-') f=0;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(ch&15);ch=getchar();}
if(f)return x;else return -x;
}
struct Trie{
int son[2][200000*30+10],tot;
void Insert(int a){
int now=0,id;
for(int i=30;i>=0;i--){
id=(a>>i)&1;
if(!son[id][now])son[id][now]=++tot;
now=son[id][now];
}
}
int Find(int r1,int r2,int b){
if(b<0) return 0;
int a1=-1,a2=-1;
if(son[0][r1]&&son[0][r2]) a1=Find(son[0][r1],son[0][r2],b-1);
if(son[1][r1]&&son[1][r2]) a2=Find(son[1][r1],son[1][r2],b-1);
if(~a1&&~a2) return min(a1,a2);
if(~a1) return a1;if(~a2) return a2;
if(son[1][r1]&&son[0][r2]) a1=Find(son[1][r1],son[0][r2],b-1)+(1<<b);
if(son[0][r1]&&son[1][r2]) a2=Find(son[0][r1],son[1][r2],b-1)+(1<<b);
if(~a1&&~a2) return min(a1,a2);
if(~a1) return a1;if(~a2) return a2;
}
}T;
long long ans;
void dfs(int a,int b){
if(b<0) return;
if(T.son[0][a]&&T.son[1][a]) ans+=1ll*T.Find(T.son[0][a],T.son[1][a],b-1)+(1ll<<b);
if(T.son[0][a]) dfs(T.son[0][a],b-1);
if(T.son[1][a]) dfs(T.son[1][a],b-1);
}
int n,v;
int main()
{
n=read();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)T.Insert(read());
dfs(0,30);
printf("%I64d\n",ans);
return 0;
}
|

